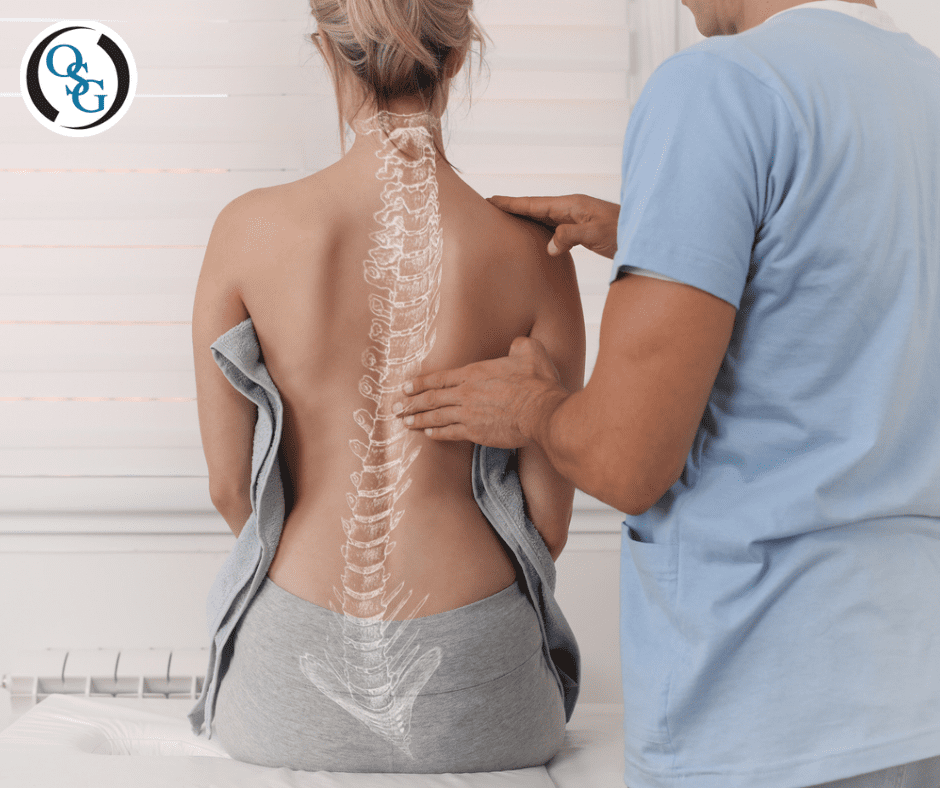
What is Scoliosis?
The spine gives your body structure and support to allow us to stand up straight and move freely. Scoliosis, a condition of the spine, affects about 2-3% of the population. Although most cases are minor, it’s important to diagnose and treat scoliosis early to prevent it from worsening, and because your spine has a hard job to do of helping you move around and live your life!
What is Scoliosis?
Scoliosis is characterized as an abnormal curvature of the spine. The spine normally should be straight, and if there is a curve, small or large, anywhere along the spine that measures more than 10 degrees on an x-ray, you are considered to have this condition. Doctors often use the letters “C” and “S” to describe the curvature’s shape and severity on the spine. Most scoliosis cases are mild, but the curvature can worsen over time and cause more complications if left untreated.
There are various types of scoliosis that are diagnosed based on severity, cause, and age:
- Idiopathic scoliosis – The cause is unknown for this scoliosis type, and it accounts for about 80% of cases.
- Congenital scoliosis – This condition is rare but occurs when a baby’s back begins to develop before birth, and the tiny vertebrae develop in a curved shape.
- Neuromuscular scoliosis – This scoliosis type is caused by a disorder such as spina bifida, cerebral palsy, or an injury to the spinal cord.
- Degenerative scoliosis – Only affecting adults, this type develops in the lower back as the spine’s disks and joints wear as you age.
Symptoms of Scoliosis
The signs of scoliosis are typically present at an early age, and most individuals are diagnosed in their adolescent or teenage years. Some visible and non-visible signs and symptoms to look for include:
- Leaning while standing
- A visible curve in the back
- One shoulder blade appears to be bigger than the other
- Ribs that stick out farther on one side than the other
- Lower back pain
- Back stiffness
- Pain and numbness in the legs caused by pinched nerves
- Fatigue and exhaustion due to muscle strain
Causes and Risk Factors of Scoliosis
As mentioned above, a majority of scoliosis cases do not have an exact cause or reason, but some instances that can lead to this spine curvature include:
- Cerebral palsy
- Spina bifida
- Muscular dystrophy
- Congenital disabilities
- Injury to the spine
- Infections
- Tumors
- Genetic conditions such as Down syndrome
For those cases where the cause is unclear, various determinants can leave you more likely to develop the condition. Risk factors for developing Idiopathic scoliosis include:
- Age – Symptoms most commonly show during the growth spurt and puberty phase of life.
- Sex – While males and females develop mild scoliosis cases at about the same rate, females are more likely to have the curvature worsen as they age and are more likely to require intense treatment.
- Genetics – In some cases, scoliosis can run in families.
If you are concerned about your spine, experiencing back pain, or have been diagnosed with scoliosis, seek treatment and guidance from professionals that can give you the proper care and help you need.
Orthopaedist in Fairfield County
It’s crucial to seek expert medical treatment if you are dealing with problems or pain associated with your bones or joints. Give the professionals at Orthopaedic Specialty Group a call at (203) 337-2600 and let us know how we can help you! Don’t let that pain hold you back from living your life. Your health and safety is our top priority.